This article provides a detailed comparison of linear slide rails with other linear motion systems, highlighting their differences in design, performance, and applications. We’ll also discuss how to select the optimal solution for your project and showcase how expert suppliers deliver tailored solutions for diverse needs.
Linear Slide Rails: An Overview
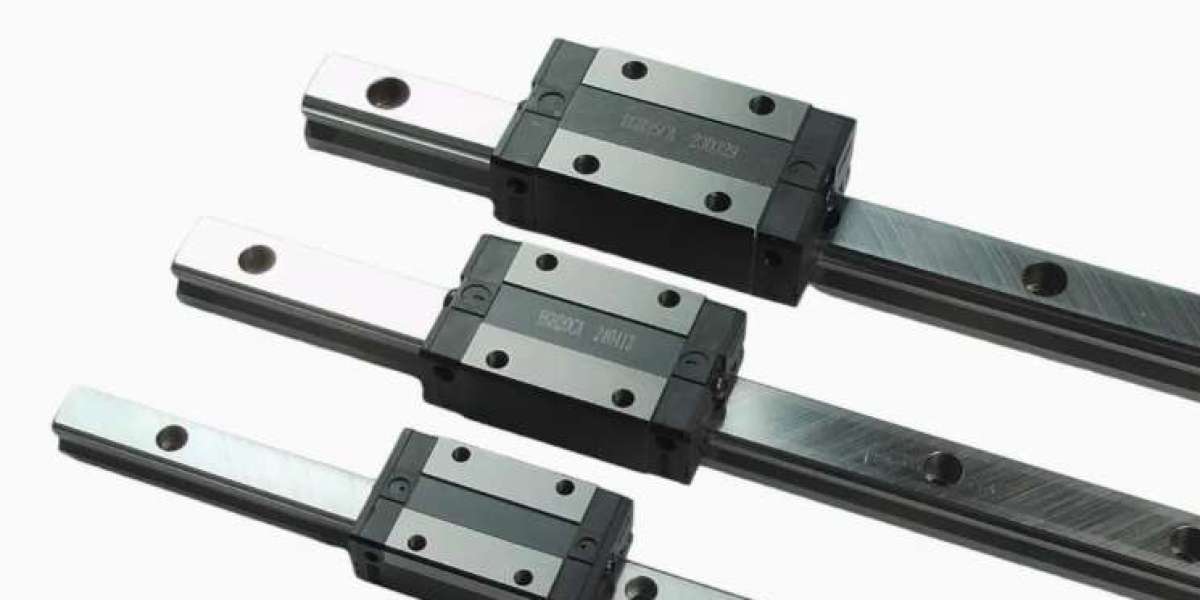
Linear slide rails are mechanical systems that enable smooth, low-friction movement along a straight axis. They consist of a rail (track)and a carriage (slider), with rolling elements (balls, rollers) or sliding materials (PTFE, bronze) reducing friction between the moving parts.
Key Advantages:
✅ Simplicity: Easy to install and maintain, with fewer components than other systems.
✅ Cost-Effectiveness: Generally more affordable than precision guide rails or linear motors.
✅ Versatility: Available in various sizes (miniature to heavy-duty) and configurations.
✅ Smooth Motion: Low friction ensures quiet, consistent movement.
Common Applications:
- •
3D printers, CNC routers, and small automation systems.
- •
Medical devices, laboratory equipment, and consumer electronics.
- •
Lightweight industrial machinery and DIY projects.
Comparison with Other Linear Motion Systems
1. Linear Slide Rails vs. Linear Guide Rails
Linear Guide Rails (also called profiled rail guides) are high-precision systems designed for heavy loads and demanding environments. They use recirculating balls or rollers along a rigid rail with multiple raceways, offering superior rigidity and accuracy.
Feature | Linear Slide Rails | Linear Guide Rails |
|---|---|---|
Load Capacity | Medium (up to 5,000N) | High (up to 50,000N+) |
Precision | Standard (±0.01mm–±0.05mm) | High (±0.001mm–±0.01mm) |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Best For | CNC routers, 3D printers, automation | CNC mills, semiconductor equipment |
When to Choose Linear Slide Rails: For applications where cost, simplicity, and moderate precision are priorities.
When to Choose Linear Guide Rails: For high-precision, heavy-duty tasks like aerospace or precision machining.
? [Explore high-precision linear guide rails] for demanding applications.
2. Linear Slide Rails vs. Ball Screws
Ball Screws convert rotational motion (from a motor) into linear motion using recirculating balls between a screw and nut. They are ideal for applications requiring precise positioning and force transmission.
Feature | Linear Slide Rails | Ball Screws |
|---|---|---|
Motion Type | Direct linear motion (rail + carriage) | Linear motion via screw rotation |
Speed | Moderate (limited by carriage design) | High (optimized for rapid movement) |
Precision | Standard | High (with preloaded nuts) |
Best For | Automation, medical devices | CNC machines, linear actuators |
When to Choose Linear Slide Rails: For smooth, low-friction movement without the need for rotational conversion.
When to Choose Ball Screws: For high-thrust applications requiring precise positioning (e.g., CNC milling).
? [Discover ball screw solutions] for high-force tasks.
3. Linear Slide Rails vs. Belt-Driven Systems
Belt-Driven Systems use a motorized pulley and belt to move a carriage along a rail. They are lightweight, fast, and cost-effective but lack the rigidity of slide rails.
Feature | Linear Slide Rails | Belt-Driven Systems |
|---|---|---|
Load Capacity | Medium | Low to medium |
Speed | Moderate | High (up to 10 m/s) |
Rigidity | High (resists deflection) | Lower (prone to vibration) |
Best For | Precision tasks, medical devices | High-speed conveyors, lightweight automation |
When to Choose Linear Slide Rails: For applications requiring stability and moderate precision.
When to Choose Belt-Driven Systems: For high-speed, low-load tasks like packaging or material handling.
Selection Criteria for Linear Slide Rails
To choose the right linear slide rail for your project, consider the following factors:
1. Load and Force Requirements
- •
Calculate the dynamic load(moving load) and static load(stationary load).
- •
Account for moment loads(e.g., off-center forces causing torque).
2. Precision and Repeatability
- •
Determine the required accuracy (e.g., ±0.01mm for general automation, ±0.001mm for CNC).
- •
Check if the system offers preloadoptions to eliminate play.
3. Speed and Acceleration
- •
High-speed applications need low-friction designs (e.g., ball-bearing carriages).
- •
Ensure the rail and carriage can withstand dynamic forces without deformation.
4. Environmental Conditions
- •
Corrosive Environments: Stainless steel or nickel-plated rails.
- •
Dusty Environments: Sealed carriages to prevent contamination.
- •
Temperature Extremes: Materials with high thermal stability (e.g., ceramic bearings).
5. Maintenance and Lifespan
- •
Regular lubrication (grease/oil) extends lifespan.
- •
Choose systems with sealed designsfor minimal maintenance.
Why Linear Slide Rails Remain a Popular Choice
Despite the availability of advanced alternatives, linear slide rails continue to be widely used due to their:
- •
Affordability: Lower upfront costs compared to precision guide rails or linear motors.
- •
Ease of Use: Simple installation and minimal maintenance requirements.
- •
Adaptability: Available in miniature, standard, and heavy-duty configurations.
Whether you’re building a DIY project or designing an industrial machine, linear slide rails offer a reliable, cost-effective solution for smooth linear motion.
Conclusion
Linear slide rails are a cornerstone of modern linear motion systems, offering a balance of simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and performance. By understanding their advantages, limitations, and comparisons with other technologies, engineers can make informed decisions to optimize their designs.
For high-quality linear slide rails tailored to your specific needs, [explore expert solutions] that combine precision engineering with durable materials. Whether you’re working on a small automation system or a large-scale industrial project, the right linear slide rail ensures smooth, reliable motion every time.