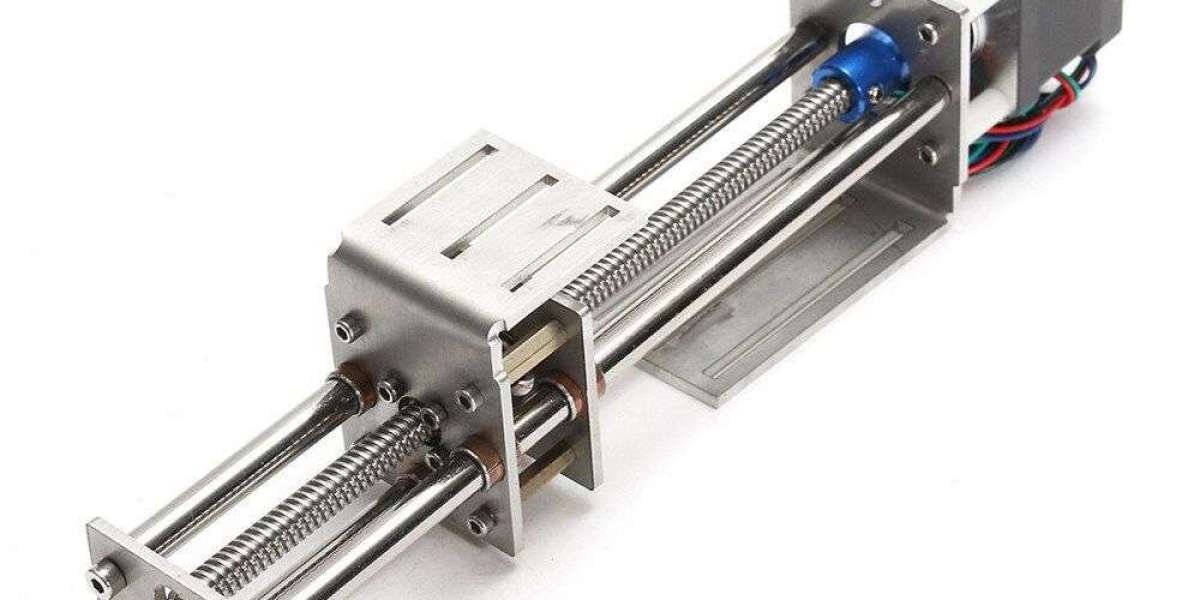
Guide Lines: Core Characteristics
Guide lines consist of:
- •
A precision-machined rail with ground raceways.
- •
A carriage containing recirculating rolling elements (balls or rollers) or sliding mechanisms.
- •
A recirculation system (for rolling elements) to enable continuous motion.
Key Advantages:
✔ High precision and load capacity
✔ Stability and rigidity under load
✔ Low friction and smooth motion
✔ Versatility in applications
Comparison with Alternative Systems
1. Guide Lines vs. Ball Screws
Ball screws convert rotary motion to linear motion using a threaded shaft and nut with recirculating balls.
Factor | Guide Lines | Ball Screws | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
Motion Type | Direct linear motion (rail + carriage) | Rotary-to-linear motion (shaft + nut) | Guide lines for multi-axis flexibility |
Load Capacity | Up to 200,000N (heavy-duty models) | Up to 100,000N | Guide lines (for heavy multi-directional loads) |
Precision | ±0.001 mm (high-precision models) | ±0.0001 mm (exceptional for thrust applications) | Ball screws for ultra-high precision |
Speed | Up to 2 m/s (optimized designs) | Up to 1 m/s | Guide lines (faster in multi-axis systems) |
Backlash | Minimal (with preloaded carriages) | Minimal (inherent in design) | Comparable, but guide lines handle side loads better |
Best For | Multi-axis systems, heavy loads | High-thrust tasks (e.g., presses) | Depends on application focus |
Insight: Ball screws excel at converting rotary motion to linear with extreme precision, making them ideal for tasks like hydraulic presses or screw-driven actuators. However, guide lines are more versatile for multi-axis systems and can handle heavier combined loads.
2. Guide Lines vs. Belt-Driven Systems
Belt drives use a motorized pulley and belt to create linear motion.
Factor | Guide Lines | Belt-Driven Systems | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
Load Capacity | Up to 200,000N | Up to 1,000N (typical) | Guide lines (for heavy loads) |
Speed | Up to 2 m/s | Up to 10 m/s | Belt drives (for high-speed tasks) |
Precision | ±0.001 mm (high-precision models) | ±0.01 mm (limited by belt elasticity) | Guide lines (for accurate positioning) |
Rigidity | High (resists deflection) | Low (belts can stretch or vibrate) | Guide lines (for stable motion) |
Cost | Moderate to High | Low | Belt drives (budget-friendly) |
Best For | Precision, heavy loads | High-speed, light loads (e.g., conveyors) | Depends on priority |
Insight: Belt-driven systems are cost-effective and ideal for high-speed applications, but they lack the precision, rigidity, and load capacity of guide lines.
3. Guide Lines vs. Linear Motors
Linear motors produce direct linear motion without mechanical contact, using electromagnetic force.
Factor | Guide Lines | Linear Motors | Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
Motion Type | Mechanical (rolling elements or sliders) | Electromagnetic (no physical contact) | Motors for speed |
Load Capacity | Up to 200,000N | Up to 50,000N | Guide lines (for heavier loads) |
Speed | Up to 2 m/s | Up to 20 m/s | Linear motors (for extreme speed) |
Acceleration | Moderate | Very High (instant thrust) | Linear motors (for rapid starts/stops) |
Best For | Reliable, moderate-speed motion | Ultra-high speed, short-stroke tasks | Depends on application needs |
Insight: Linear motors are the fastest linear motion solution (e.g., maglev trains or high-speed sorting systems), but they’re more complex, expensive, and have lower load capacity compared to guide lines, which are better for everyday industrial use.
Hybrid Systems: Combining Technologies
Many advanced systems combine guide lines with other technologies to leverage their strengths:
- •
Guide Lines + Ball Screws: For multi-axis motion with high thrust (e.g., CNC mills).
- •
Guide Lines + Belt Drives: For high-speed tasks with moderate precision.
- •
Multi-Axis Systems (X, Y, Z): Using guide lines for primary axes and specialized guides for auxiliary movements.
How to Choose the Right System
When deciding between guide lines and alternatives, consider:
- 1.
Primary Requirement: Precision, speed, load capacity, or cost?
- 2.
Application Type: Heavy industry (e.g., manufacturing) vs. lightweight automation (e.g., 3D printing).
- 3.
Environment: Harsh conditions may favor sealed or corrosion-resistant guide lines.
Conclusion: Why Guide Lines Are a Smart Default
Guide lines offer a balanced combination of precision, load capacity, and versatility, making them ideal for most industrial and commercial applications. Whether you’re building a CNC machine, a robotic arm, or a 3D printer, guide lines provide the smooth, reliable motion you need. For more insights or to explore premium guide line solutions, visit YH Linear Newsor browse our product catalog at YH Linear. #GuideLines #LinearMotion #PrecisionEngineering #Manufacturing #Engineering #IndustrialTech